How a Facial Recognition System is Changing the Digital World
 The modern world is built on digital interactions. From the moment we unlock our smartphones to the instant we log into our social media accounts, we are engaging with a digital ecosystem that is constantly evolving. At the heart of this evolution is a technology that is both subtle and powerful: facial recognition. Once the stuff of science fiction, the widespread adoption of a facial recognition system is now fundamentally reshaping our daily lives, transforming everything from how we secure our data to how we navigate public spaces. This technology is not just an upgrade—it’s a new paradigm that brings unprecedented convenience and a host of complex ethical questions.
The modern world is built on digital interactions. From the moment we unlock our smartphones to the instant we log into our social media accounts, we are engaging with a digital ecosystem that is constantly evolving. At the heart of this evolution is a technology that is both subtle and powerful: facial recognition. Once the stuff of science fiction, the widespread adoption of a facial recognition system is now fundamentally reshaping our daily lives, transforming everything from how we secure our data to how we navigate public spaces. This technology is not just an upgrade—it’s a new paradigm that brings unprecedented convenience and a host of complex ethical questions.
Understanding the Core Technology
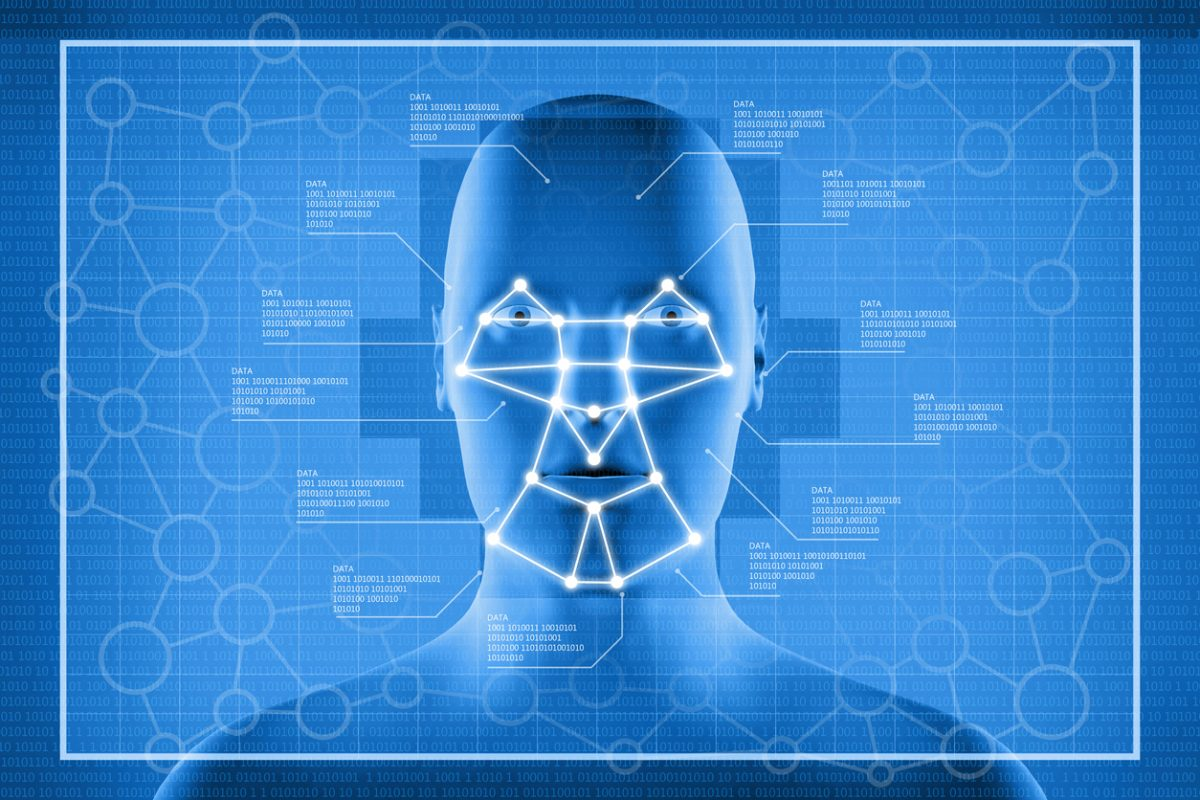
At its most basic level, facial recognition is a biometric technology that uses a person’s facial features to identify or verify their identity. While it may seem like magic, the process is a series of precise, algorithm-driven steps:
- Face Detection: The system first detects a human face in an image or video frame.
- Feature Analysis: It then analyzes facial geometry by measuring key features—such as the distance between the eyes, the shape of the jawline, and the depth of the eye sockets.
- Data Conversion: These measurements are converted into a unique digital signature, often called a “faceprint.”
- Matching: Finally, the faceprint is compared against a database of known faceprints to find a match.
This entire process is powered by machine learning and deep learning algorithms that are trained on massive datasets, allowing the facial recognition system to become more accurate and efficient over time.
From Convenience to Customization: A Transformed Digital Experience
The most visible impact of this technology is in the way it streamlines our digital lives, making them more secure and personalized.
- Enhanced Personal Security: The days of remembering complex passwords for every app are slowly fading. A facial recognition system allows you to unlock your phone, authorize banking transactions, and log into private accounts with a simple glance. This not only makes life more convenient but also provides a level of security that is difficult for hackers to bypass.
- Seamless User Experience: Social media platforms use facial recognition to automatically tag friends in photos, create personalized filters, and recommend content based on emotional analysis of a user’s expression. This leads to a more engaging and customized digital environment.
- Simplified Payments: Some financial services and retail stores are now allowing customers to pay with their faces. This frictionless transaction removes the need for wallets or cards, offering a new level of ease and speed for in-store purchases.
A New Era for Business and Public Spaces
The influence of facial recognition extends far beyond personal devices, creating new possibilities and challenges for businesses and public services.
- Retail and Marketing: Retailers are using facial recognition to analyze customer demographics and foot traffic in stores, allowing them to optimize store layouts and target advertisements more effectively. This provides businesses with invaluable data to improve the customer experience and boost sales.
- Law Enforcement and Security: Law enforcement agencies use a facial recognition system to identify suspects, locate missing persons, and enhance security in airports, stadiums, and other public venues. This application has the potential to make our communities safer, but it also raises significant questions about civil liberties.
- Corporate and HR Management: Companies are using facial recognition for employee attendance and access control. Employees can enter buildings and clock in for shifts just by showing their faces, creating a more efficient and secure workplace.
The Double-Edged Sword: Privacy and Ethics
As with all powerful technologies, the rise of facial recognition comes with serious ethical concerns. While it promises convenience and security, it also poses a threat to our fundamental rights.
- Data Privacy: The most pressing concern is the collection and storage of facial data. Who owns this data? How is it stored, and is it truly secure? The possibility of a data breach could expose an individual’s biometric information, which cannot be changed like a password.
- Mass Surveillance: The widespread use of facial recognition in public spaces could lead to a future of pervasive surveillance. The thought of being identified and tracked in a crowd without consent raises alarms about the erosion of personal freedom and anonymity.
- Bias and Accuracy: Research has shown that some facial recognition systems exhibit bias, with higher error rates for women and people of color. This can lead to misidentification, false arrests, and other forms of discrimination, undermining the very justice and security it promises to provide.
 Conclusion:
Conclusion:
The facial recognition system is no longer a futuristic concept; it is an integrated part of our digital present. It has brought about an era of unprecedented convenience and security while simultaneously forcing us to confront difficult questions about privacy, surveillance, and fairness. As this technology continues to evolve, the conversation around its use must be a central part of our digital discourse. The challenge for society is to strike a balance between harnessing the immense power of facial recognition for progress and implementing robust regulations to protect individual rights and human dignity.