Understanding How People Search: What is User Intent?
Google receives about 5,600,000,000 or 5.6 billion searches every day across the globe. These searches can be as simple as the nearest restaurant or complex, like what happens if the earth stops spinning. All these queries have a reason behind them, which is known as search intent.
In 2013, Google introduced Hummingbird and RankBrain to the world, which showed everyone that Google gave priority to understanding the user’s intent to provide better search results. And since then, SEO has never been the same.
It is impossible to rank high on SERPs by simply matching the keywords on your web pages with search queries. You need to do more than that to make your website SEO-friendly. You need to optimize your content to match the search intent to rank high on SERP and drive traffic to your website.
Here’s what we will cover about user intent in this article:
- Types of user intent
- Types of SERP intent
- Using SERP features to identify user intent
- Tips to improve your website to match user intent
Types of User Intent
Before you learn how user intent affects your website ranking, you need to understand the different search intent you can come across through queries. Some of the most common ones are:
1. Local intent (here)
This type of intent refers to the queries that are searching for a physical location. You can search for restaurants or shops near you or the location of a geographical area. You can usually find the results for such searches as listings on SERP.
2. Comparative intent
People often search on Google looking for the best brand or model for a product they want to buy. Such searches have comparative intent where the user wants to know which product is best for them or worst for them. These comparisons can be for price, quality, or features.
3. Informational intent
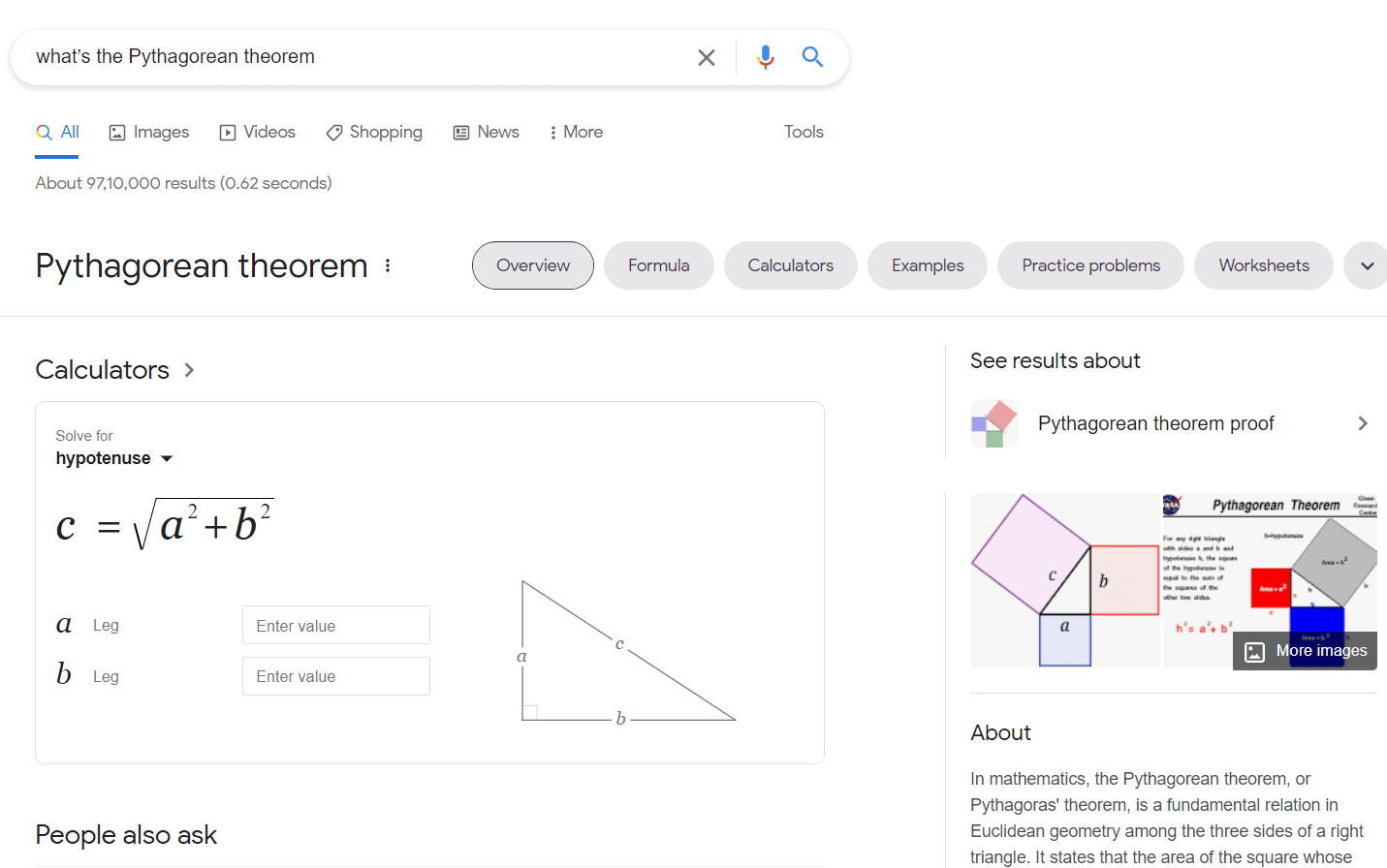
As the name suggests, such search queries are all about gaining information. The person is usually looking for information about a particular topic. Let’s say you search for ‘what’s the Pythagorean theorem?’ The results for such queries are mostly informational videos, research websites, graphs, and much more.
4. Transactional intent
The search queries where a person plans to buy something have transactional intent. Such questions open up an array of websites that sell that product. However, if the person would make a purchase remains unclear.
5. Navigational intent
These search queries are about finding a specific brand website or a particular variety of a product or a specific movie review video, etc.
Most searches on the search engines fall under these categories. However, search engines look at search queries a bit differently. You can look at them as SERP intent. Here are primary SERP intents that you should know about.
1. Topic ambiguity
Human beings have a mysterious thought process, which you can often see in their search queries. For example, a bat can refer to multiple things like animals, sports equipment, a cigarette company (British American Tobacco).
And search engines find it hard to differentiate between all these, as they are all spelled the same. Though the other keywords used in the query can help, they can significantly affect the search results.
2. Fractured intent
Fractured intent is when the phrase used for search is particular and precise, but we cannot gauge its purpose. The user can look for several things which we cannot determine just with the search query. For example, if someone searches for ‘content solutions,’ they can look for various software or the best softwares or information on how content softwares work.
SERPs provide interconnected results in case of fractured intent that the user may or may not find helpful, resulting in lower click-through rates for such keywords.
3. Favored intent
Favored intent simply means that SERP prefers to show comparative pages when faced with fractured intent. Websites with multiple pages with varied information on the keyword are likely to rank better for such keywords. However, that doesn’t mean having a comparative page for every keyword is enough to rank you better. Your content strategy plays a vital role in ranking as well.
4. Explicit intent
It is probably the easiest to identify by the search engines as users clearly describe what they are looking for through long-tail keywords. For example, ‘buy Nike Air Jordan 1 online’ clearly states the shoes the individual is looking for and wants to purchase online. Such queries get the best results, as you can quickly provide what the customer is looking for.
Using SERP Features to Identify User Intent
Even after knowing multiple users and SERP intents, making conclusions only considering the query would be wrong. Take the help of existing SERP features to understand them better. Here’s how you can do that.
1. Use Google tabs
Whenever you search anything on Google, you can view different tabs under the search bar, which show results separated by search intents.
The home tab is best for informational intent search queries, while the shopping tab is best for transactional intent queries.
You can create content for each keyword that matches the tab requirements to match user intent easily. It will help you increase your click-through rates and rankings.
2. Google snippets
Snippets are a relatively newer addition to the Google SERP page. The audience likes snippets as they provide meaningful information that matches the user’s intent without going to any website.
For example, when you search for Star Wars, you can see snippets containing information on movies and trending topics rather than the franchise itself. It is because most users want specific movie information, which Google understands.
By adding Schema to your website, you can ensure that your snippets get better clicks.
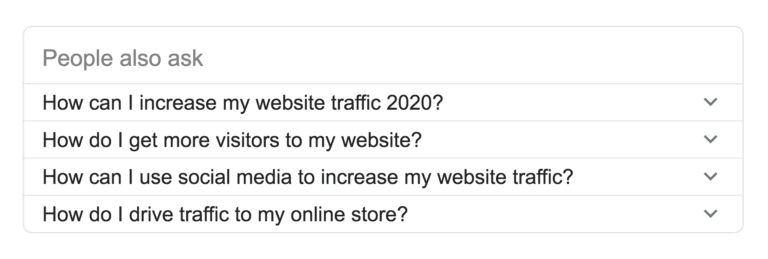
3. Related questions
Related questions are a set of Google suggested queries that appear under the first few SERP results. Titled under ‘People also ask,’ these queries are related topics to the primary search query. These queries can give you a fair idea of what people are looking for when searching for those keywords. And by answering those related questions, you can find a place on the SERP page.
Tips to Improve Your Website to Match User Intent
User intent and customer’s buying journey walk hand in hand. So understanding user intent and optimizing your website to match the buyer’s journey at each level is crucial for your business. Here are some things that you can do to make your website match user intent.
1. Improve your page structure
Not every customer that comes to your website is looking to purchase at that moment. However, that should not stop you from guiding them to buy in the future. And to do that, you need to make sure that your website’s structure is user-friendly and easy to navigate. You can add informational links that tell the user more about your product or services and strategically place call-to-action buttons that guide them towards purchasing.
2. Make your snippets to match user intent
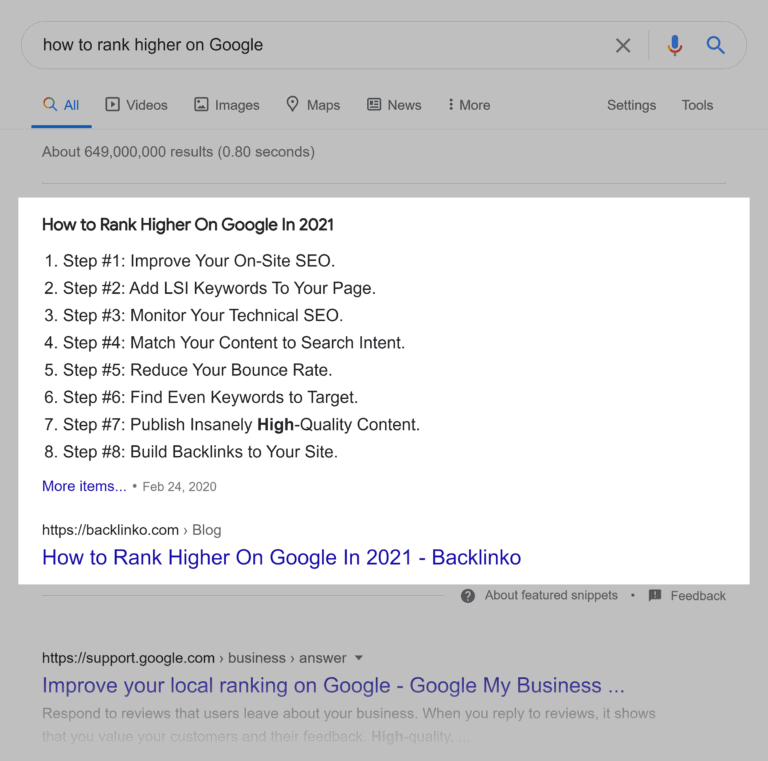
As mentioned earlier, snippets are Google’s answer to matching the user intent in the best way possible. Most snippets provide concise information that users may look for as text and images. Here is a featured snippet for ‘how to rank higher on Google’ –
Ensure that your snippets get featured on the SERP page. And to do this, you need to optimize the content on your website accordingly. To increase the number of featured snippets, you need to add to the point paragraphs on your website that answer a question precisely. And don’t forget about adding schema markup to your snippet content.
3. Target users with different intent through multiple landing pages
Using the same landing pages for all your links will not satisfy different user intents. Therefore, create multiple landing pages that match various user intents and the level of the buyer journey.
- Use introductory pages and home pages for landing pages created for new users.
- Discount and offer pages for cost-conscious customers.
- Specific product landing pages for re-targeted customers.
4. Use competitor analysis for identifying keywords
Sometimes it’s hard to find the right keywords that match the user intent in a particular business segment, even with the best keyword research tools at your hand. In such cases, your best bet is to conduct a competitor analysis and find the keywords they are ranking for.
Once you have a list of keywords they rank for, you can analyze them to determine the user intent. Then you can make your SEO strategy rank for those keywords better.
5. Don’t overlook informational intent
Your priority would be to capture all the transactional or buyer’s intent as a business is all about selling. However, you need to keep in mind that about 92% of people who visit the website for the first time have no intention of buying. However, if your website only caters to transactional intent, they would simply lose interest and won’t come back.
That’s why you need to add informational content to your website, even if it’s an e-commerce website.
Conclusion
To rank high on the search engine result page, you need to ensure that your website can satisfy both user intent and SERP intent. You also need to keep in mind that search engine algorithms evolve every day to understand user intent better. Therefore, to stay ahead of the game, you need to keep updating your website regularly. Designing your website to match user intent will eventually help you get better customers who want to be a part of your brand.